Understanding Financial Risk Ratings: What They Are and Why They Matter
In the world of finance, risk management is crucial for both individuals and businesses. One of the most important tools used to evaluate and manage risk is the financial risk rating. Financial risk ratings help investors, analysts, and financial institutions assess the risk associated with investments, companies, or even entire industries. These ratings provide insights into the potential risks involved, helping stakeholders make more informed decisions.

What is a Financial Risk Rating?
A financial risk rating is a numerical or qualitative assessment of the potential risk associated with an investment, company, or financial product. It provides a snapshot of the overall risk level, indicating how likely the investment is to fail or underperform.
These ratings are typically provided by credit rating agencies, independent analysts, or financial institutions. The risk ratings help investors evaluate the financial health of an entity, the likelihood of default, and the general volatility of returns. The lower the rating, the higher the perceived risk.
Types of Financial Risk Ratings
Different types of financial risk ratings are used to assess various forms of risk. Understanding the different categories can help you assess the overall financial standing of an investment. Here are the main types of financial risk ratings:
1. Credit Risk Ratings
Credit risk ratings evaluate the likelihood that a borrower will default on a loan or bond. These ratings are typically issued by agencies like Standard & Poor’s (S&P), Moody’s, or Fitch. Credit ratings range from AAA (lowest risk) to D (default).
Key Features:
-
High credit ratings indicate a low risk of default.
-
Low credit ratings indicate higher risk and may require higher interest rates to compensate for the risk.
-
These ratings are essential for bond investors and lenders to determine the level of risk associated with lending money.
2. Market Risk Ratings
Market risk ratings focus on the risk associated with the volatility of the financial markets. This includes the potential fluctuations in asset prices, interest rates, and economic conditions. Investors need to assess market risk when investing in stocks, commodities, or foreign exchange markets.
Key Features:
-
Market risk ratings indicate the volatility or price movement of an asset.
-
These ratings are useful for assessing the overall market conditions that could impact your investments.
-
A high market risk rating means the asset is likely to experience significant price fluctuations.
3. Operational Risk Ratings
Operational risk refers to the risks arising from a company’s internal processes, systems, and people. This includes fraud, system failures, or human error that could affect business operations.
Key Features:
-
Operational risk ratings are vital for understanding the likelihood of internal disruptions.
-
A higher rating indicates the company may face more significant internal issues that could impact performance.
-
These ratings are especially useful for companies assessing their internal controls and risk mitigation strategies.
4. Liquidity Risk Ratings
Liquidity risk refers to the possibility that an asset cannot be quickly bought or sold in the market without affecting its price. This is particularly relevant for illiquid assets like real estate or private equity.
Key Features:
-
A low liquidity risk rating indicates that an asset can be easily traded.
-
A higher liquidity risk rating indicates that the asset may be difficult to sell quickly, which could lead to potential losses.
-
These ratings are particularly important for investors looking for liquid assets or those who may need to sell investments quickly.
5. Systemic Risk Ratings
Systemic risk ratings assess the likelihood of an entire financial system or market failing, often triggered by economic downturns, policy changes, or geopolitical events.
Key Features:
-
Systemic risk affects entire sectors or economies, rather than individual companies.
-
High systemic risk could mean that the broader economy or financial system faces significant threats.
-
This type of rating is important for macro-level financial planning and understanding overall market stability.
How Financial Risk Ratings Are Calculated
The process of calculating financial risk ratings can vary depending on the type of risk being assessed. Generally, these ratings are derived from a combination of qualitative and quantitative data, including financial statements, historical performance, market trends, and expert opinions.
Key Components of Financial Risk Rating Calculations:
-
Financial Ratios: Common financial ratios like debt-to-equity and current ratios are used to measure liquidity and solvency.
-
Macroeconomic Factors: Analysts consider factors like interest rates, inflation, and unemployment rates to assess market conditions.
-
Historical Performance: Past performance data of the company or asset being rated is considered to predict future risk.
Example: Credit Ratings Calculation
Credit rating agencies may look at factors like the company’s ability to meet debt obligations, past borrowing history, and overall financial health to determine the credit risk rating.
The Role of Financial Risk Ratings in Portfolio Management
Financial risk ratings play a crucial role in portfolio management. Portfolio managers use these ratings to ensure that they are balancing risk across various assets. By investing in a mix of high-rated and low-rated investments, portfolio managers can create a diversified portfolio that meets the investor’s risk tolerance and financial goals.

How They Help:
-
Risk Diversification: By analyzing risk ratings, investors can spread their investments across different types of risk to minimize potential losses.
-
Informed Decision-Making: Risk ratings provide valuable insights into which investments may align with an investor’s financial goals and risk appetite.
-
Better Risk Management: Financial risk ratings help investors identify high-risk assets and adjust their portfolios accordingly.
Why Financial Risk Ratings Matter
Financial risk ratings are essential tools for investors, companies, and financial institutions. Here’s why they matter:
-
Investment Decisions: Investors rely on these ratings to assess which assets or companies are worth investing in based on their risk profiles.
-
Creditworthiness: Lenders use credit risk ratings to determine whether or not to extend credit to a business or individual.
-
Risk Mitigation: By understanding risk ratings, companies and investors can implement strategies to mitigate potential risks and make informed financial decisions.
FAQs About Financial Risk Ratings
1. How do financial risk ratings affect investment choices?
Financial risk ratings provide a snapshot of the risk level associated with different investments. Investors use these ratings to determine the level of risk they are willing to take and make choices that align with their financial goals.
2. What is the difference between credit risk and market risk?
Credit risk is the likelihood that a borrower will default on a loan, while market risk pertains to the potential for price fluctuations due to market conditions. Credit risk focuses on the individual borrower’s ability to repay, while market risk assesses external factors affecting the asset’s price.
3. How often are financial risk ratings updated?
Financial risk ratings are typically updated on a regular basis, depending on changes in financial conditions, economic factors, and performance metrics. For instance, credit ratings may be updated annually or when significant events, like mergers or changes in company performance, occur.
4. Can financial risk ratings predict financial success?
While financial risk ratings provide insights into potential risks, they cannot guarantee financial success. Ratings help assess the likelihood of default or underperformance, but they do not account for unforeseen events or future opportunities.
5. How can businesses improve their financial risk rating?
Businesses can improve their financial risk rating by strengthening their financial health, paying off debts, improving cash flow, and reducing exposure to volatile markets. Maintaining consistent, transparent financial records also helps in improving risk ratings over time.
Conclusion
Understanding financial risk ratings is crucial for anyone involved in investing or financial management. These ratings provide valuable insights into the risk level associated with investments, loans, and financial products. By leveraging the information provided by risk ratings, you can make informed decisions that align with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
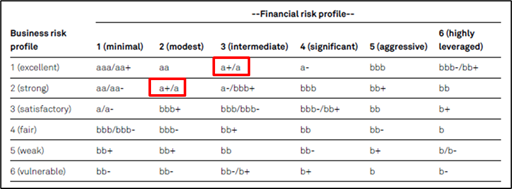
Whether you’re an investor seeking to diversify your portfolio or a company aiming to improve your financial stability, financial risk ratings offer a structured way to assess and manage risk effectively. Use these ratings to guide your decisions and build a robust, risk-conscious financial future.